Adding Foreman Hosts with ansible and AWX
I wanted to checkout the provisioning capabilities of ansible. So I wanted to accomplish the same tasks as I did in my previous post and create a VM in VMware and then add a host to foreman which will create the boot profile for the VM.
Creating a VM with ansible
Ansible used to utilize the vsphere_guest module (it’s now deprecated). It just depends on the pysphere python library. So let’s install that with pip2:
<> sudo pip2 install pysphere
and after that you can create a playbook like this:
---
- hosts: localhost
connection: local
vars:
vcenter_hostname: hp.kar.int
esxhost: hp.kar.int
datastore: datastore1
network: VM_VLAN3
dumpfacts: False
vcenter_user: root
vcenter_passwd: password
vm_name: test01
tasks:
- name: Create a VM
delegate_to: localhost
vsphere_guest:
vcenter_hostname: "{{ vcenter_hostname }}"
username: "{{ vcenter_user }}"
password: "{{ vcenter_passwd }}"
esxi:
datacenter: ha-datacenter
hostname: "{{ vcenter_hostname }}"
validate_certs: no
guest: "{{ vm_name }}"
state: powered_on
vm_extra_config:
vcpu.hotadd: yes
mem.hotadd: yes
notes: This is a test VM
vm_disk:
disk1:
size_gb: 10
type: thin
datastore: "{{ datastore }}"
vm_nic:
nic1:
type: vmxnet3
network: "{{ network }}"
network_type: standard
vm_hardware:
memory_mb: 1536
num_cpus: 1
osid: centos7_64Guest
scsi: paravirtual
- name: Collect Facts
delegate_to: localhost
vsphere_guest:
vcenter_hostname: "{{ vcenter_hostname }}"
validate_certs: no
username: "{{ vcenter_user }}"
password: "{{ vcenter_passwd }}"
guest: "{{ vm_name }}"
vmware_guest_facts: yes
register: vmfacts
- name: Print MAC mac_address
debug:
msg: "{{ vmfacts.ansible_facts.hw_eth0.macaddress }} {{ vm_name }}"
- name: Restart VM
delegate_to: localhost
vsphere_guest:
vcenter_hostname: "{{ vcenter_hostname }}"
username: "{{ vcenter_user }}"
password: "{{ vcenter_passwd }}"
guest: "{{ vm_name }}"
state: restarted
And then run it:
<> ansible-playbook esxi.yml
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [localhost] ***************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [localhost]
TASK [Create a VM] *************************************************************
changed: [localhost -> localhost]
TASK [Collect Facts] ***********************************************************
ok: [localhost -> localhost]
TASK [Print MAC mac_address] ***************************************************
ok: [localhost] => {
"msg": "00:0c:29:f2:f2:9b test01"
}
TASK [Restart VM] **************************************************************
changed: [localhost -> localhost]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
localhost : ok=5 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
Since that’s deprecated, I also ended up playing with the vmware_guest module. Here are some examples on how to create a vm on esxi with the vmware_guest module:
- vmware_guest for stand-alone ESXi hosts?
- vmware_guest state: poweredon/poweredoff/restarted doesn’t do anything
Install the latest version of pyvomi
The vmware_guest module depends on the pyvomi python module. Initially I just installed the one ubuntu had in it’s repos but I then ran into this issue. Here was the version I had initially:
<> pip list | grep omi
pyvmomi (5.5.0-2014.1.1)
Then I uninstalled that and install the latest one:
<> sudo apt remove python-pyvmomi
<> sudo pip install pyvmomi
And then I got the working version:
<> pip list | grep omi
pyvmomi (6.7.0)
Then running the playbook worked out:
<> ansible-playbook esxi-new.yml
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [localhost] ***************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [localhost]
TASK [Create a VM] *************************************************************
changed: [localhost -> localhost]
TASK [Collect Facts] ***********************************************************
ok: [localhost -> localhost]
TASK [Print MAC mac_address] ***************************************************
ok: [localhost] => {
"msg": "00:0c:29:f2:f2:9b test01"
}
Both approaches worked, but I am sure the deprecated one will be phased out.
Adding a Host to Foreman with ansible
There is a foreman module available, but it’s not very robust at the moment (looks like there are some pull requests to expand it). There is another foreman module which has more parameters. This one depends on a python module called python-foreman and it’s actually a custom python module created by the same author (not to be confused by the official one). Instructions on how to install the module are covered here. First install the python module:
sudo pip2 install git+https://github.com/Nosmoht/python-foreman.git#master
Then we need to install the ansible module. First create the directory:
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/ansible/modules
sudo chown elatov -R /usr/local/ansible/modules
Now let’s put our module in there:
git clone https://github.com/Nosmoht/ansible-module-foreman.git
mv ansible-module-foreman /usr/local/ansible/modules
Then modify the search path (this is discussed in the official documentation: Ansible Configuration Settings):
<> grep ^library /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
library = /usr/local/ansible/modules
Then create a simple playbook like this:
<> cat foreman.yml
---
- hosts: localhost
connection: local
vars:
foreman_host: fore.kar.int
foreman_port: 443
foreman_user: admin
foreman_pass: password
arch: x86_64
domain: kar.int
env: production
os: CentOS 7
part: Kickstart default
loc: Default Location
org: Default Organization
root_pass: password
medium: centos7-pulp
mac: 00:0c:29:f2:f2:9b
subnet: vlan-3
vm_name: test01
tasks:
- name: Ensure Host
foreman_host:
name: "{{ vm_name }}"
architecture: "{{ arch }}"
domain: "{{ domain }}"
environment: "{{ env }}"
operatingsystem: "{{ os }}"
ptable: "{{ part }}"
location: "{{ loc }}"
organization: "{{ org }}"
medium: "{{ medium }}"
subnet: "{{ subnet }}"
mac: "{{ mac }}"
provision_method: build
root_pass: "{{ root_pass }}"
foreman_host: "{{ foreman_host }}"
foreman_port: "{{ foreman_port }}"
foreman_user: "{{ foreman_user }}"
foreman_pass: "{{ foreman_pass }}"
state: present
and run it:
<> ansible-playbook foreman.yml
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [localhost] ***************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [localhost]
TASK [Ensure Host] *************************************************************
[WARNING]: Module did not set no_log for root_pass
changed: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
localhost : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
If you login to the foreman host, you will see the new host created:
[elatov@fore ~]$ hammer host list
---|----------------|------------------|------------|----------|-------------------|--------------|----------------------
ID | NAME | OPERATING SYSTEM | HOST GROUP | IP | MAC | CONTENT VIEW | LIFECYCLE ENVIRONMENT
---|----------------|------------------|------------|----------|-------------------|--------------|----------------------
1 | fore.kar.int | CentOS 7.4.1708 | | 10.0.0.7 | 00:0c:29:53:5e:1a | |
11 | test01.kar.int | CentOS 7 | | | 00:0c:29:f2:f2:9b | |
---|----------------|------------------|------------|----------|-------------------|--------------|----------------------
Pretty sweet.
Creating a VMware VM with AWX
There is an unofficial way of installing custom python modules in the awx container. This is discussed here:
So let’s try that out:
<> docker-compose exec task /bin/bash
[root@awx awx]# . /var/lib/awx/venv/ansible/bin/activate
(ansible) [root@awx awx]# pip install pysphere
And that actually worked out, I created a new template and set the extra variables there and it ran the same playbook.
Creating a Custom VirtualEnv
It looks like now with later versions you can create your own virtualenv. The setup is covered in Managing Custom Python Dependencies. So let’s create a new virtualenv and use it to deploy a VM using vmware_guest module instead of the vsphere_guest one.
<> docker-compose exec task /bin/bash
[root@awx awx]# virtualenv /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env
New python executable in /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/bin/python2
Also creating executable in /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/bin/python
Installing setuptools, pip, wheel...done.
Initially I ran into a couple of compile issues, when I tried to install the base packages
[root@awx awx]# /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/bin/pip install python-memcached psutil
Here is the first one I saw:
copying psutil/tests/__main__.py -> build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/psutil/tests
running build_ext
building 'psutil._psutil_linux' extension
creating build/temp.linux-x86_64-2.7
creating build/temp.linux-x86_64-2.7/psutil
gcc -pthread -fno-strict-aliasing -O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -D_GNU_SOUR$
E -fPIC -fwrapv -DNDEBUG -O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -D_GNU_SOURCE -fPIC -f$
rapv -fPIC -DPSUTIL_POSIX=1 -DPSUTIL_VERSION=545 -DPSUTIL_LINUX=1 -DPSUTIL_ETHTOOL_MISSING_TYPES=1 -I/usr/include/python2.7 -c psutil/_psutil_common.c -o build/temp.linux-x86_64-2.7/psutil/_psutil$
common.o
unable to execute gcc: No such file or directory
error: command 'gcc' failed with exit status 1
----------------------------------------
Failed building wheel for psutil
Running setup.py clean for psutil
and also this
psutil/_psutil_common.c:9:20: fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory
#include <Python.h>
^
compilation terminated.
error: command 'gcc' failed with exit status 1
To fix both issues, I just ran this
[root@awx awx]# yum install gcc python-devel
And then I was able to install the base pip modules. Then I installed the latest version of ansible:
[root@awx awx]# /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/bin/pip install ansible
Now let’s install the necessary plugin:
[root@awx awx]# /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/bin/pip install pyvmomi
[root@awx awx]# /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/bin/pip show pyvmomi
Name: pyvmomi
Version: 6.7.0
Summary: VMware vSphere Python SDK
Home-page: https://github.com/vmware/pyvmomi
Author: VMware, Inc.
Author-email: jhu@vmware.com
License: License :: OSI Approved :: Apache Software License
Location: /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/lib/python2.7/site-packages
Requires: requests, six
Required-by:
Ended up with the following modules:
[root@awx awx]# /var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/bin/pip list
Package Version
---------------- ---------
ansible 2.5.1
asn1crypto 0.24.0
bcrypt 3.1.4
certifi 2018.4.16
cffi 1.11.5
chardet 3.0.4
cryptography 2.2.2
enum34 1.1.6
idna 2.6
ipaddress 1.0.22
Jinja2 2.10
MarkupSafe 1.0
paramiko 2.4.1
pip 10.0.1
psutil 5.4.5
pyasn1 0.4.2
pycparser 2.18
PyNaCl 1.2.1
python-memcached 1.59
pyvmomi 6.7.0
PyYAML 3.12
requests 2.18.4
setuptools 39.0.1
six 1.11.0
urllib3 1.22
wheel 0.31.0
I ran the same commands on the web and task containers:
<> docker-compose exec task /bin/bash
..
<> docker-compose exec web /bin/bash
...
At this point you can query your templates with tower-cli:
<> tower-cli job_template list
== ============= ========= ======= ============
id name inventory project playbook
== ============= ========= ======= ============
9 karim-foreman 2 6 fore.yml
8 karim-vm 2 6 esxi-new.yml
== ============= ========= ======= ============
This will list the ID of your templates. Now let’s add the new custom virtualenv to the foreman template:
<> curl -X PATCH http://192.168.1.106:82/api/v2/job_templates/9/ -u elatov -d @t.json -H 'Content-Type: application/json'
The content of t.json was just a simple config:
<> cat t.json
{
"custom_virtualenv": "/var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env"
}
And then you should see the custom one added:
<> curl -u elatov -X GET http://192.168.1.106:82/api/v2/config/
Enter host password for user 'elatov':
{"custom_virtualenvs":["/var/lib/awx/venv/karim-env/"],"eula":"","license_info":{"license_type":"open","compliant":true,"valid_key":true,"license_key":"OPEN","features":{"rebranding":true,"surveys":true,"multiple_organizations":true,"activity_streams":true,"ldap":true,"workflows":true,"ha":true,"system_tracking":true,"enterprise_auth":true}},"analytics_status":"off","version":"1.0.5.29","project_base_dir":"/var/lib/awx/projects","time_zone":"UTC","ansible_version":"2.5.1","project_local_paths":[]}%
If you checkout the config in the UI you will see it there as well:
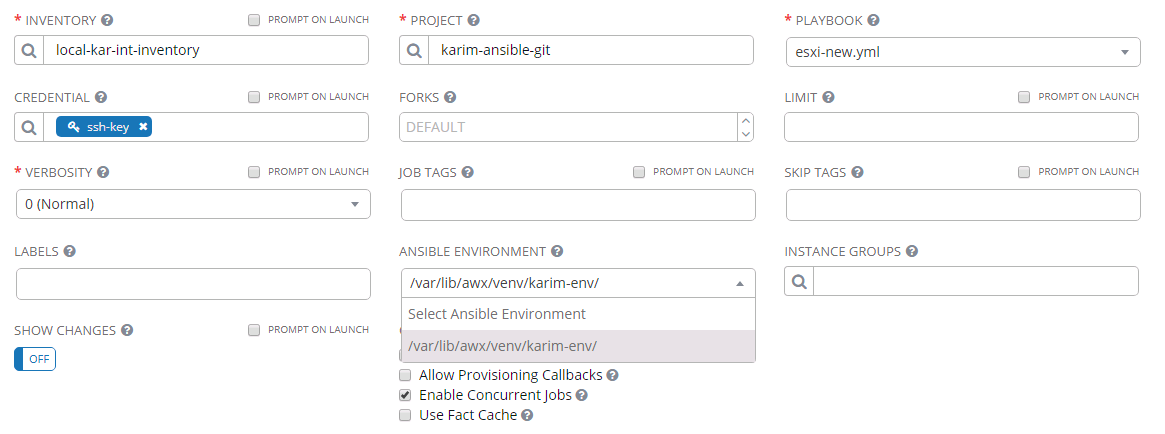
Initially I ran into this:
<> curl -X PATCH http://192.168.1.106:82/api/v2/job_templates/8/ -u elatov -d @t.json -H 'Content-Type: application/json'
Enter host password for user 'elatov':
{"custom_virtualenv":["/var/lib/awx/venv/karim-venv is not a valid virtualenv in /var/lib/awx/venv"]}%
And that was because I didn’t add the virtualenv on the web container.
Creating a Foreman Host with awx
Very similar approach, install the necessary python modules in your custom virtualenv first. As for the custom ansible modules, it looks like we can just create a library directory inside the git repo and just put all the files there (this is discussed in Using an unreleased module from Ansible source with Tower). Then push all the new files to the git repo:
[master 08b06a9] test adding external module
27 files changed, 5710 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 library/__init__.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_architecture.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_compute_attribute.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_compute_profile.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_compute_resource.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_config_template.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_domain.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_environment.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_external_usergroup.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_filter.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_host.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_hostgroup.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_image.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_ldap.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_location.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_medium.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_operatingsystem.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_organization.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_os_default_template.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_ptable.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_realm.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_role.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_setting.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_smart_proxy.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_subnet.py
create mode 100644 library/foreman_user.py
create mode 100755 library/foreman_usergroup.py
pushing changes
Counting objects: 30, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (29/29), done.
Writing objects: 100% (30/30), 28.09 KiB | 2.81 MiB/s, done.
Total 30 (delta 25), reused 0 (delta 0)
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (25/25), completed with 1 local object.
To https://github.com/elatov/ansible.git
04f36d1..08b06a9 master -> master
And with those two things in place, I was able to run a test foreman ansible playbook:
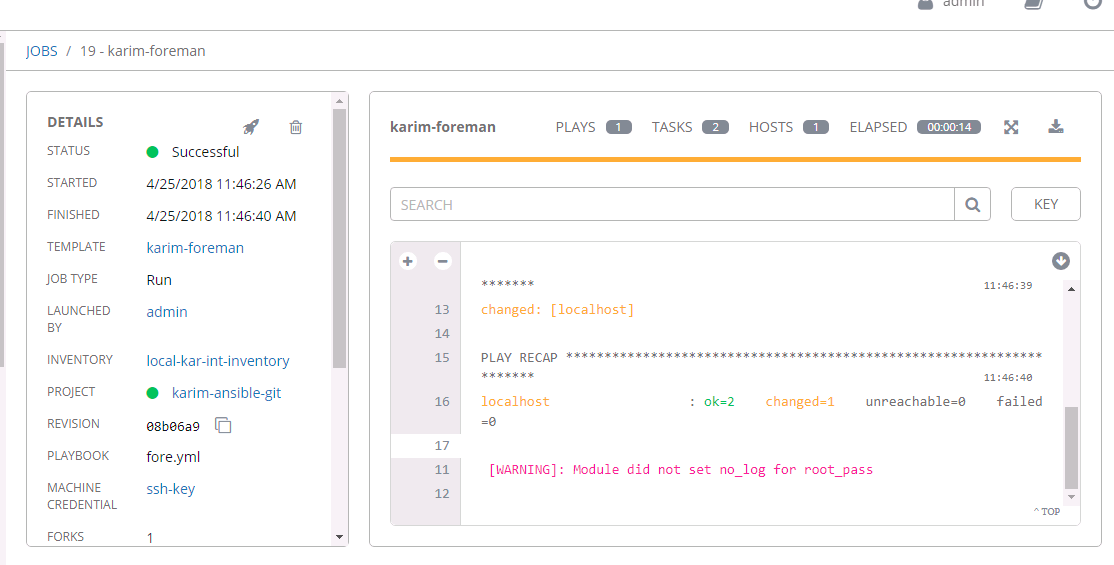
Combining all the Tasks into one playbook
There are a couple of options for combining different playbooks but it seems that sharing variable between playbooks is kind of a pain and the easiest approach is to just create one playbook with multiple tasks:
- Pass through a variable to an included playbook
- set_fact - Set host facts from a task
- Passing variables between nested playbooks
After doing that I ran the combined playbook:
<> ansible-playbook fore-esxi.yml
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [localhost] ***************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [localhost]
TASK [Create a VM] *************************************************************
changed: [localhost -> localhost]
TASK [Collect Facts] ***********************************************************
ok: [localhost -> localhost]
TASK [Print MAC mac_address] ***************************************************
ok: [localhost] => {
"msg": "00:0c:29:f2:f2:9b test01"
}
TASK [set_fact] ****************************************************************
ok: [localhost]
TASK [Create Foreman Host] *****************************************************
[WARNING]: Module did not set no_log for root_pass
changed: [localhost]
TASK [Restart VM] **************************************************************
changed: [localhost -> localhost]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
localhost : ok=7 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0
I also created a clean up playbook to remove the created resources and that worked out as well:
<> ansible-playbook fore-esxi-clean.yml
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty, only localhost is available. Note
that the implicit localhost does not match 'all'
PLAY [localhost] ***************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [localhost]
TASK [Delete VM] ***************************************************************
changed: [localhost -> localhost]
TASK [Delete Foreman Host] *****************************************************
[WARNING]: Module did not set no_log for root_pass
changed: [localhost]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
localhost : ok=3 changed=2 unreachable=0 failed=0
You can checkout both of the playbooks in the above git repo.