Using the Nginx Ingress Controller with Kubernetes
Kubernetes Ingress Controller
There are some good examples of how to use it and what is does here:
Configure an Nginx Ingress Controller
Instructions are in the Installation Guide. First get the source:
<> git clone https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx.git
Then apply all the applicable configuration files:
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/namespace.yaml
namespace "ingress-nginx" created
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/default-backend.yaml
deployment "default-http-backend" created
service "default-http-backend" created
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/configmap.yaml
configmap "nginx-configuration" created
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/tcp-services-configmap.yaml
configmap "tcp-services" created
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/udp-services-configmap.yaml
configmap "udp-services" created
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/rbac.yaml
serviceaccount "nginx-ingress-serviceaccount" created
clusterrole "nginx-ingress-clusterrole" created
role "nginx-ingress-role" created
rolebinding "nginx-ingress-role-nisa-binding" created
clusterrolebinding "nginx-ingress-clusterrole-nisa-binding" created
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/with-rbac.yaml
deployment "nginx-ingress-controller" created
<> kubectl apply -f ingress-nginx/deploy/provider/baremetal/service-nodeport.yaml
service "ingress-nginx" created
You should be able to see all the configs deployed:
<> kubectl get all -n ingress-nginx
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deploy/default-http-backend 1 1 1 1 6m
deploy/nginx-ingress-controller 1 1 1 1 4m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
rs/default-http-backend-55c6c69b88 1 1 1 6m
rs/nginx-ingress-controller-d7b4cbf98 1 1 1 4m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deploy/default-http-backend 1 1 1 1 6m
deploy/nginx-ingress-controller 1 1 1 1 4m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
rs/default-http-backend-55c6c69b88 1 1 1 6m
rs/nginx-ingress-controller-d7b4cbf98 1 1 1 4m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
po/default-http-backend-55c6c69b88-wj8bn 1/1 Running 0 6m
po/nginx-ingress-controller-d7b4cbf98-xqmrr 1/1 Running 0 4m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc/default-http-backend ClusterIP 10.102.171.108 <none> 80/TCP 6m
svc/ingress-nginx NodePort 10.106.90.156 <none> 80:36006/TCP,443:36698/TCP 2m
Just a quick note, I ended up adding hostNetwork: true to the ingress-nginx/deploy/with-rbac.yaml file to make sure the ingress controller can listen on ports 80 and 443 (this is discussed in HostPort seemingly not working ). And you can see the endpoints:
<> kubectl get ep -n ingress-nginx
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
default-http-backend 10.244.0.45:8080 1d
ingress-nginx 192.168.1.106:80,192.168.1.106:443 1d
Creating Ingress Rules
Good thing to check out are the different options you can set with Annotations. There were also a couple of issues with missing the trailing slash (/), but some workarounds are available here:
Creating Ingress Rules for Jenkins
I had already followed instructions in Running Jenkins behind a Proxy and enabled the service to run under /jenkins, here is the relevant config:
<> grep prefix /data/k8s/jenkins/jenkins-deployment.yaml -B 2
env:
- name: JENKINS_OPTS
value: "--prefix=/jenkins"
Then I created the following Ingress configuration:
<> cat /data/k8s/jenkins/jenkins-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: jenkins
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: "/jenkins"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: |
rewrite ^(/jenkins)$ http://$best_http_host$1/ permanent;
spec:
rules:
- host: ub.kar.int
http:
paths:
- path: /jenkins
backend:
serviceName: jenkins
servicePort: 8080
Now if I go to http://K8S_HOST/jenkins, I would be forwarded to the jenkins service:
Creating Ingress Rules for the Kubernetes Dashboard
Since this uses SSL by default, I ended up using SSL Passthrough, here is the configuration I ended up with:
<> cat /data/k8s/dashboard/ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: dashboard
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: "/"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/secure-backends: "true"
namespace: kube-system
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- ub.kar.int
rules:
- host: ub.kar.int
http:
paths:
- path: /ui
backend:
serviceName: kubernetes-dashboard
servicePort: 8443
Now if I go to https://K8S_HOST/ui, I would be forwarded to the kubernetes dashboard:
Creating Ingress Rules for Grafana (Heapster)
I had installed heapster and that uses Grafana for it’s dashboard. First it looks like we need to enable the application to be aware that it’s getting reverse proxied (Running Grafana behind a reverse proxy). Luckily we can just update an environment variable and apply a new config:
<> grep -i root grafana.yaml -A 3
- name: GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL
# If you're only using the API Server proxy, set this value instead:
# value: /api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/monitoring-grafana/proxy
value: "%(protocol)s://%(domain)s:%(http_port)s/grafana"
And then to apply the config:
<> kubectl apply -f grafana.yaml
deployment "monitoring-grafana" configured
service "monitoring-grafana" unchanged
Then creating the following Ingress rule:
<> cat ingress.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: grafana
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: "/"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "false"
namespace: kube-system
spec:
rules:
- host: ub.kar.int
http:
paths:
- path: /grafana
backend:
serviceName: monitoring-grafana
servicePort: 3000
Took care of the config and if I go to http://K8S_HOST/grafana, I would be forwarded to the grafana service:
Checking out the Nginx Controller
First if you want to you can check out the logs:
<> kubectl get po -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
default-http-backend-55c6c69b88-wj8bn 1/1 Running 2 1d
nginx-ingress-controller-6b96d48658-gznhl 1/1 Running 0 1d
<> kubectl logs -n ingress-nginx nginx-ingress-controller-6b96d48658-gznhl
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NGINX Ingress controller
Release: 0.9.0
Build: git-6816630
Repository: https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I1227 16:29:28.597996 7 main.go:227] Creating API client for https://10.96.0.1:443
I1227 16:29:28.607067 7 main.go:239] Running in Kubernetes Cluster version v1.9 (v1.9.0) - git (clean) commit 925c127ec6b946659ad0fd596fa959be43f0cc05 - platform linux/amd64
I1227 16:29:28.608379 7 main.go:83] validated ingress-nginx/default-http-backend as the default backend
I1227 16:29:29.112689 7 stat_collector.go:77] starting new nginx stats collector for Ingress controller running in namespace (class nginx)
I1227 16:29:29.112716 7 stat_collector.go:78] collector extracting information from port 18080
I1227 16:29:29.121746 7 nginx.go:250] starting Ingress controller
I1227 16:29:29.125970 7 event.go:218] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Ingress", Namespace:"kube-system", Name:"dashboard", UID:"503b6563-eb20-11e7-8985-0c4de99d45d5", APIVersion:"extensions", ResourceVersion:"3503144", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'CREATE' Ingress kube-system/dashboard
I1227 16:29:29.126020 7 event.go:218] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Ingress", Namespace:"default", Name:"jenkins", UID:"eeba89d4-eaac-11e7-b87a-0c4de99d45d5", APIVersion:"extensions", ResourceVersion:"3503143", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'CREATE' Ingress default/jenkins
I1227 16:29:29.221928 7 nginx.go:255] running initial sync of secrets
I1227 16:29:29.221986 7 nginx.go:288] starting NGINX process...
I1227 16:29:29.222052 7 leaderelection.go:174] attempting to acquire leader lease...
I1227 16:29:29.222689 7 controller.go:211] backend reload required
I1227 16:29:29.222890 7 stat_collector.go:34] changing prometheus collector from to default
I1227 16:29:29.226398 7 status.go:196] new leader elected: nginx-ingress-controller-7b99574fd5-zl6vt
I1227 16:29:29.260288 7 controller.go:220] ingress backend successfully reloaded...
I1227 16:30:10.743031 7 leaderelection.go:184] successfully acquired lease ingress-nginx/ingress-controller-leader-nginx
I1227 16:30:10.743088 7 status.go:196] new leader elected: nginx-ingress-controller-6b96d48658-gznhl
I1227 16:30:29.230343 7 status.go:352] updating Ingress default/jenkins status to [{ }]
I1227 16:30:29.230354 7 status.go:352] updating Ingress kube-system/dashboard status to [{ }]
I1227 16:30:29.234089 7 event.go:218] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Ingress", Namespace:"kube-system", Name:"dashboard", UID:"503b6563-eb20-11e7-8985-0c4de99d45d5", APIVersion:"extensions", ResourceVersion:"3504130", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'UPDATE' Ingress kube-system/dashboard
I1227 16:30:29.236038 7 event.go:218] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Ingress", Namespace:"default", Name:"jenkins", UID:"eeba89d4-eaac-11e7-b87a-0c4de99d45d5", APIVersion:"extensions", ResourceVersion:"3504131", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'UPDATE' Ingress default/jenkins
I1227 16:30:56.164627 7 controller.go:211] backend reload required
I1227 16:30:56.164792 7 event.go:218] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Ingress", Namespace:"kube-system", Name:"dashboard", UID:"503b6563-eb20-11e7-8985-0c4de99d45d5", APIVersion:"extensions", ResourceVersion:"3504130", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'DELETE' Ingress kube-system/dashboard
I1227 16:30:56.197815 7 controller.go:220] ingress backend successfully reloaded...
I1227 16:31:16.499599 7 event.go:218] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Ingress", Namespace:"kube-system", Name:"dashboard", UID:"5c6ac3ac-eb23-11e7-8985-0c4de99d45d5", APIVersion:"extensions", ResourceVersion:"3504196", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'CREATE' Ingress kube-system/dashboard
I1227 16:31:16.499917 7 controller.go:211] backend reload required
I1227 16:31:16.535950 7 controller.go:220] ingress backend successfully reloaded...
I1227 16:31:29.231279 7 status.go:352] updating Ingress kube-system/dashboard status to [{ }]
I1227 16:31:29.234964 7 event.go:218] Event(v1.ObjectReference{Kind:"Ingress", Namespace:"kube-system", Name:"dashboard", UID:"5c6ac3ac-eb23-11e7-8985-0c4de99d45d5", APIVersion:"extensions", ResourceVersion:"3504213", FieldPath:""}): type: 'Normal' reason: 'UPDATE' Ingress kube-system/dashboard
2017/12/27 16:32:20 [error] 572#572: *5 upstream sent no valid HTTP/1.0 header while reading response header from upstream, client: 192.168.1.117, server: ub.kar.int, request: "GET / HTTP/2.0", upstream: "http://10.244.0.40:8443/", host: "ub.kar.int"
This can give you a bunch of hints as to why nginx is having issue reverse proxying to an application. You can also attach to the container and check out the nginx config:
<> kubectl exec -it -n ingress-nginx nginx-ingress-controller-6b96d48658-gznhl /bin/sh
# grep jenkins /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
upstream default-jenkins-8080 {
location /jenkins {
set $proxy_upstream_name "default-jenkins-8080";
set $ingress_name "jenkins";
set $service_name "jenkins";
rewrite ^(/jenkins)$ http://$best_http_host$1/ permanent;
proxy_pass http://default-jenkins-8080;
The config is pretty big, but you get the point, from there you can figure out what affect the annotations from above have on this file. You can also visit http://K8S_HOST:18080/nginx_status and you can see a small status servlet:
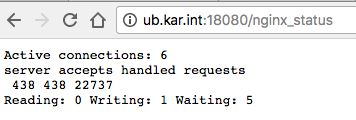
Checking out the Ingress Rules
You can also use kubectl to confirm the Igress rules, to list them just run this:
<> kubectl get ing --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
default jenkins ub.kar.int 80 1d
kube-system dashboard ub.kar.int 80, 443 1d
kube-system grafana ub.kar.int 80 1d
If you want more information we can use describe:
<> kubectl describe ing dashboard -n kube-system
Name: dashboard
Namespace: kube-system
Address:
Default backend: default-http-backend:80 (<none>)
TLS:
SNI routes ub.kar.int
Rules:
Host Path Backends
---- ---- --------
ub.kar.int
/ui kubernetes-dashboard:8443 (10.244.0.40:8443)
Annotations:
Events: <none>
Pretty sweet.